Hi to you all, November is almost upon us and with that we acknowledge Diabetes Awareness Month. Our discussion this week is Balanced Bites For Sugar and insulin balance.
Function of The Pancreas
The main gland involved with sugar and insulin balance is the pancreas. The pancreas belongs to the endocrine and digestive systems—with most of its cells (more than 90%) working on the digestive side. However, the pancreas performs the vital duty of producing hormones—most notably insulin—to maintain the balance of blood glucose (sugar) and salt in the body. Without this balance, your body is susceptible to serious complications, such as diabetes. Functions of the pancreas include:
- The pancreas maintains the body’s blood glucose (sugar) balance.
- Primary hormones of the pancreas include insulin and glucagon, and both regulate blood glucose.
- Diabetes is the most common disorder associated with the pancreas.
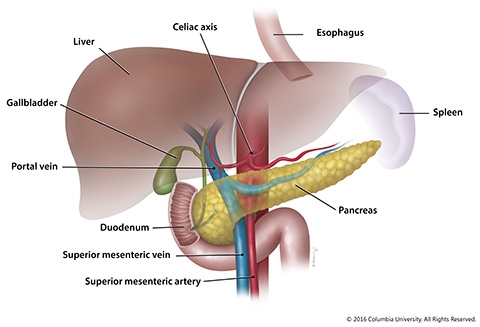
Anatomy of the Pancreas
The pancreas is a 6 inch-long flattened gland that lies deep within the abdomen, between the stomach and the spine. It is connected to the duodenum, which is part of the small intestine. The pancreas is typically divided into five parts:
- Head – the widest part of the pancreas. It lies within the C-shaped curve created by the duodenum and is connected to it by connective tissue.
- Uncinate process – a projection arising from the lower part of the head and extending medially to lie beneath the body of the pancreas. It lies posterior to the superior mesenteric vessels.
- Neck – located between the head and the body of the pancreas. It overlies the superior mesenteric vessels which form a groove in its posterior aspect.
- Body – centrally located, crossing the midline of the human body to lie behind the stomach and to the left of the superior mesenteric vessels.
- Tail – the left end of the pancreas that lies within close proximity to the hilum of the spleen.
What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin resistance is when cells in your muscles, fat, and liver don’t respond well to insulin and can’t use glucose from your blood for energy. To make up for it, your pancreas makes more insulin. Over time, your blood sugar levels go up. Some signs of insulin resistance include:
Signs & Symptoms
- A waistline over 40 inches in men and 35 inches in women
- Blood pressure readings of 130/80 or higher
- A fasting glucose level over 100 mg/dL
- A fasting triglyceride level over 150 mg/dL
- A HDL cholesterol level over under 40 mg/dL in men and 50 mg/dL in women
- Skin tags
- Patches of dark, velvety skin called acanthosis nigricans
Risk Factors & causes of Insulin Resistance
- Obesity, especially belly fat
- Inactive lifestyle
- Diet high in carbohydrates
- Gestational diabetes
- Health conditions like nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and polycystic ovary syndrome
- A family history of diabetes
- Smoking
- Ethnicity — it’s more likely if your ancestry is African, Latino, or Native American
- Age — it’s more likely after 45
- Hormonal disorders like Cushing’s syndrome and acromegaly
- Medications like steroids, antipsychotics, and HIV medications
- Sleep problems like sleep apnea
How The Pancreas Works – Diabetes Explained
Diseases & Disorders of the Pancreas
Type 1 Diabetes
If you have type 1 diabetes, then your body doesn’t produce any insulin to handle the glucose in your body. Insulin deficiency causes a range of complications, so people with type 1 diabetes have to take insulin to help their body use glucose appropriately.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is much more prevalent than type 1. People with type 2 diabetes may be able to produce insulin, but their bodies don’t use it correctly. They might also be unable to produce enough insulin to handle the glucose in their body. Lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise, play a major role in managing and preventing type 2 diabetes.
Hyperglycemia
This condition is caused by abnormally high blood glucose levels. It can be caused by overproduction of the hormone glucagon.
Hypoglycemia
Conversely, hypoglycemia is caused by low blood glucose levels. It is caused by a relative overproduction of insulin.
Balanced Bites For Sugar & Insulin Balance
You can take steps to reverse insulin resistance (metabolic syndrome) and prevent type 2 diabetes. The most important treatment is controlling/balancing your sugar and insulin levels. Keeping your sugar and insulin levels constant throughout the day instead of having spikes or dips at every mealtime is the ideal and avoid food types that cause this to happen. If metabolic syndrome goes untreated, it could lead to:
- Severe high blood sugar
- Severe low blood sugar
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Kidney disease
- Eye problems
- Cancer
- Alzheimer’s disease
You can’t tell that you have insulin resistance by how you feel. You’ll need to get a blood test that checks your blood sugar levels. Likewise, you won’t know if you have most of the other conditions that are part of insulin resistance syndrome (high blood pressure, low “good” cholesterol levels, and high triglycerides) without seeing your health care practitioner.
If you suspect you may have metabolic syndrome or any of the above disorders.Contact your local Healthcare Practitioner.
Balanced Healing can assist you with a personalised lifestyle plan to balance your sugar and insulin levels.
Contact Sr Bridget Spargo @ 083 653 7470 or Email: b@balancedhealing.co.za to book an appointment.
References
Website: https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/insulin-resistance-syndrome
Website: https://teachmeanatomy.info/abdomen/viscera/pancreas/
Website: https://www.endocrineweb.com/endocrinology/overview-pancreas
Website: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X9ivR4y03DE